KNOW MORE

Zinc (Zn) is taken up by plants as the divalent Zn²⁺ cation. It was one of the first micronutrients recognized as essential for plants and the one most commonly limiting yields.
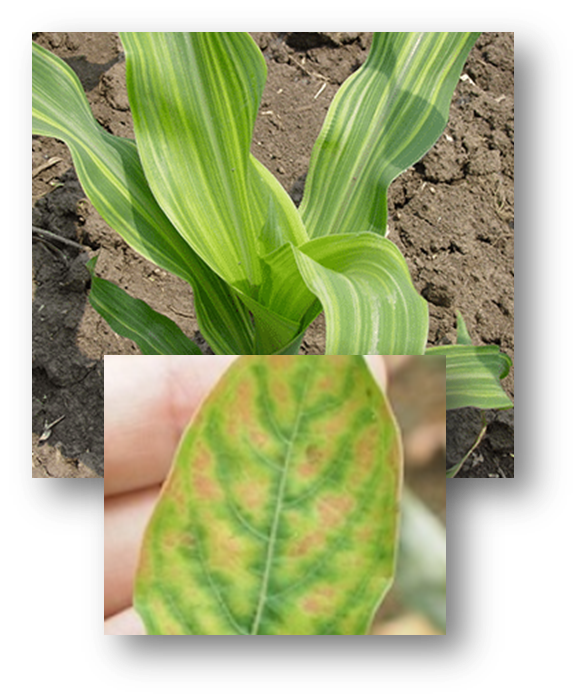
Although Zn is required in small amounts, high yields are impossible without it. Protein synthesis and growth regulation require Zn. Reduced hormone production due to a Zn-deficient plant will cause the shortening of internodes and stunted leaf growth. Zinc is much less mobile within the plant, so deficiency symptoms first appear on the younger leaves. Zinc aids synthesis of plant-growth substances and enzyme systems, and is essential for promoting certain metabolic reactions, which are particularly critical in the early growth stages. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses.ZINC
Powerful Micronutrient
Protein Synthesis and Growth Regulation
Deficiency Symptoms
Metabolic Reactions
Zinc deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
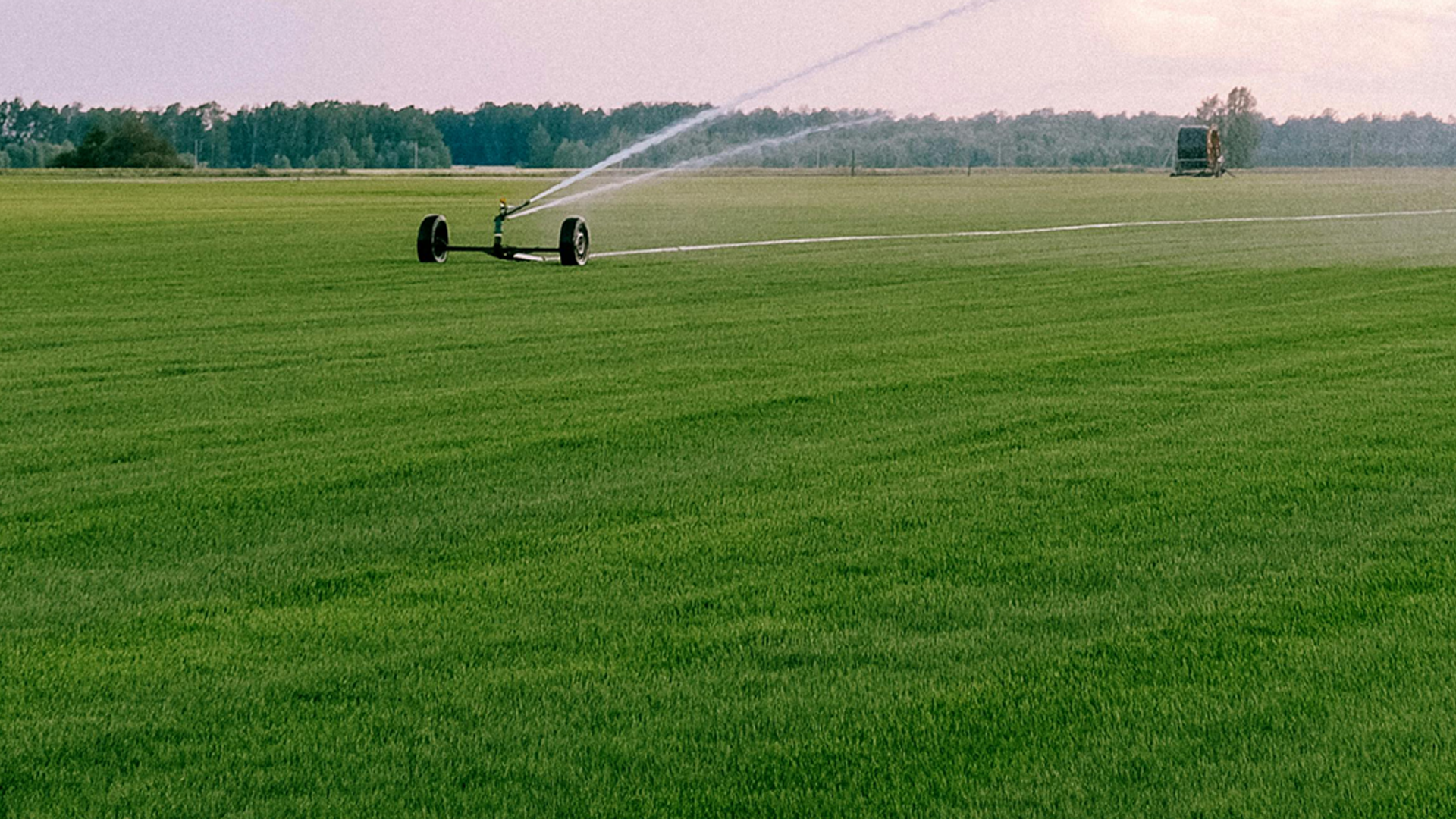
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.