KNOW MORE
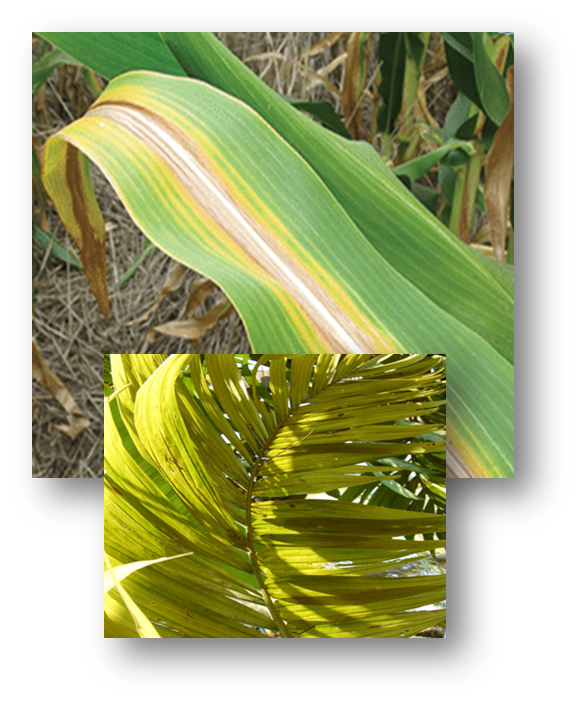

Nitrogen (N) is essential for plant growth and is part of every living cell. It plays many roles in plants and is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis.
Plants take up most of their N as the ammonium (NH₄⁺) or nitrate (NO₃⁻) ion. Some direct absorption of urea can occur through the leaves, and small amounts of N are obtained from materials such as water-soluble amino acids. Nitrogen is a component of vitamins, amino acids and energy systems within the plant, which form its proteins. Thus, N is directly responsible for increasing protein content in plants. Lack of N and chlorophyll means the plant will not utilize sunlight as an energy source to carry on essential functions such as nutrient uptake. Nitrogen is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis and, as a part of chlorophyll molecules, is involved in photosynthesis. Nitrate is very mobile in the soil and moves with soil water to root surfaces for plant absorption. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses.NITROGEN
Macronutrient Uptake
Increasing Protein Content
Nutrient Uptake
Photosynthesis
Mobility
Nitrogen deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.