KNOW MORE

Calcium (Ca) is found all around us, and the very existence of plants and animals depends on it.
Plants take up Ca as the Ca²⁺ cation. Once inside the plant, Ca functions in several essential ways. Calcium deficiencies occur most often in acidic, sandy soils from which Ca leaches via rain or irrigation water. Calcium helps balance organic acids within the plant as well as activates several plant enzyme systems. Calcium helps form the compounds that make up part of cell walls, which in turn, strengthen the plant structure. Calcium builds yields indirectly by improving root growth conditions and stimulating microbial activity, molybdenum (Mo) availability and uptake of other nutrients. Calcium helps enable nitrogen (N)-fixing bacteria that form nodules on the roots of leguminous plants to capture atmospheric N gas and convert it into a form plants can use. Calcium stimulates root and leaf development, and affects uptake and activity of other nutrients. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses. CALCIUM
Essential Secondary Nutrient
Calcium Deficiencies
Balance Organic Acids
Cell Walls
Building Yields
Form Nodules
Stimulate Development
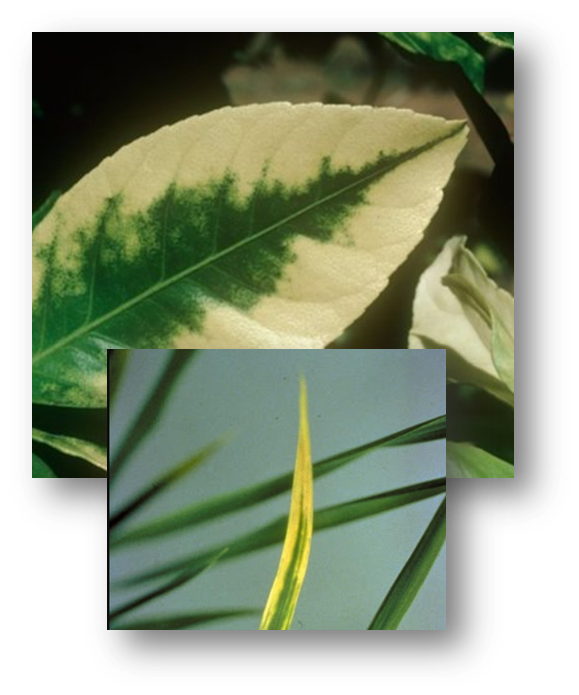
Calcium deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.