KNOW MORE
Phosphorus (P) is a limiting nutrient in the soil-plant nutrient cycling. Although the exogenous application of chemical P fertilizers can satisfy crop P requirements during critical growth phases. While excessive P fertilizers use results in low phosphorus acquisition efficiency (PAE), it has serious environmental consequences and hastens the depletion of P mineral reserves. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) have the potential to make insoluble phosphate available to plants through solubilization and mineralization, increasing crop yields while maintaining environmental sustainability.
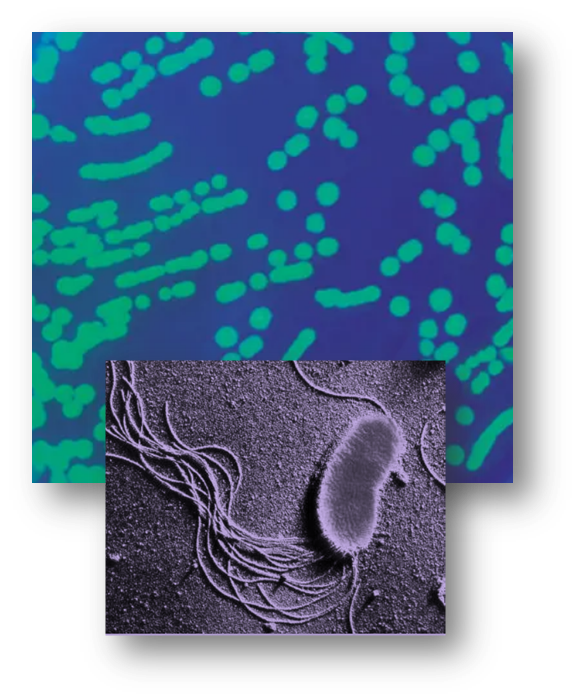
Pseudomonas fluorescens is a phosphate solubilizing bacterial species that can be used to make biofertilizers. It can be isolated from plant rhizospheres and is considered a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR) because it can increase the availability of phosphorus in plants. This can help sustain the health and productivity of crops,Strains from the genera Pseudomonas, Bacillus and Rhizobium are among the most powerful phosphate solubilizers. The principal mechanism for mineral phosphate solubilization is the production of organic acids, and acid phosphatases play a major role in the mineralization of organic phosphorous in soil. Phosphorus (P) is a vital biogenic element that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of various compounds, such as phytic acid, nucleic acid, and phospholipids, in plants . It is closely intertwined with key metabolic processes, including nitrogen (N) and carbon (C) metabolism, as well as photosynthesis, thereby exerting a positive influence on crop growth and development. Insufficient P nutrition in crops hinders the biosynthesis of nucleic acid, phospholipids, and triphosphate nucleotides, thereby affecting cell division, energy conversion, and cellular respiration, ultimately leading to a reduction in the photosynthetic rate This is a bacterium effectively used in controlling sheath blight and blast of paddy, wilt diseases of redgram, and banana. Pseudomonas fluorescens is a gram negative, rod shaped nonspore forming bacteria which may be mono or lopotrichous or non-motile. It produces greenish, fluorescent and water soluble pigment, pyoverdin. The direct influence of pseudomonas on plant growth is mediated either by release of auxin-like substances or through improved uptake of nutrients in the environment. Pseudomonas fluorescens
Bio-P
phosphate solubilizing bacteria
Crop Growth and Development
Disease controll
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.