KNOW MORE

Copper (Cu) activates enzymes and catalyzes reactions in several plant-growth processes. Vitamin A production is closely linked to the presence of Cu as well, and it helps ensure successful protein synthesis.
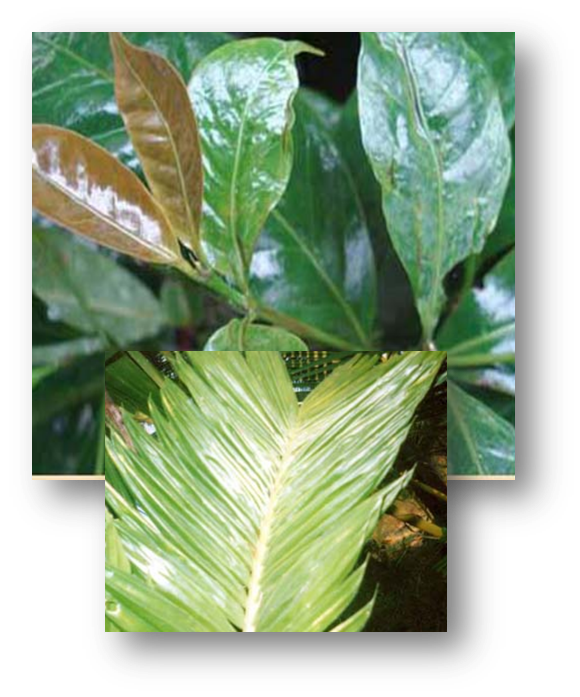
Classified as a micronutrient, only a small amount of this essential nutrient is needed for plant survival. Copper is the most immobile of the micronutrients. Many vegetable crops show Cu hunger, with leaves that lose turgor and develop a bluish-green shade before becoming chlorotic and curling. Copper is necessary to chlorophyll formation in plants and catalyzes several other plant reactions. Other metals in the soil, such as iron, manganese and aluminum, affect the availability of Cu for plant growth. Organic soils are the most vulnerable to Cu deficiency; heavy, clay-type soils are least vulnerable. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses.COPPER
Essential Micronutrient
Immobility
Copper Hunger
Chlorophyll Formation
Influences From Other Metals
Types of Soils
Copper deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.