KNOW MORE

One of three primary nutrients, phosphorus (P) is essential for plant growth, and a plant must access it to complete its normal production cycle.
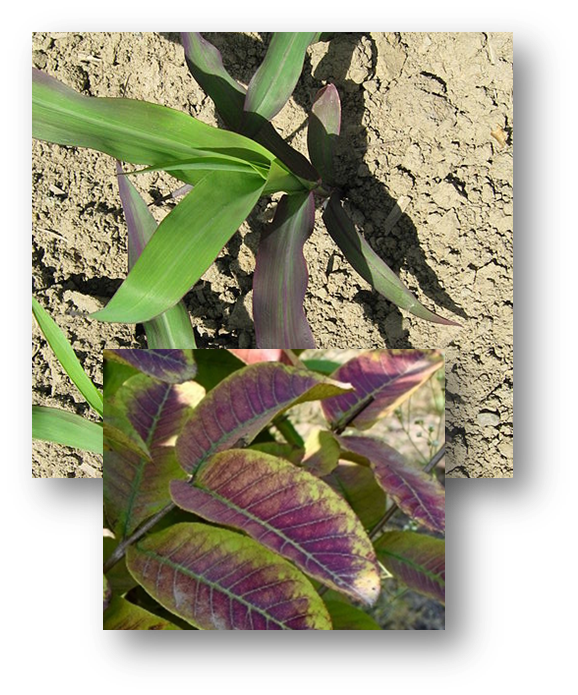
Plants absorb P from the soil as primary and secondary orthophosphates (H₂PO₄⁻ and HPO₄²⁻). The highest levels of P in young plants are found in tissue at the growing point. As crops mature, most P moves into the seeds, fruit, or both. Under P deficiency, some crops, such as corn, tend to show discoloration. Phosphorus is noted especially for its role in capturing and converting the sun's energy into useful plant compounds. Phosphorus promotes root development and early seedling growth. Research associates specific growth factors with P: stimulated root development, increased stalk and stem strength, and improved flower formation and seed production. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses.PHOSPHORUS
Phosphorus in Soil
Growing Point
Discoloration
Plant Compounds
Root & Seedling Growth
Growth Factors
Phosphorus deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.