KNOW MORE

Plants take up chlorine (Cl) as the chloride (Cl-) anion. It’s active in energy reactions in the plant. Most Cl- in soils comes from salt trapped in parent materials, marine aerosols and volcanic emissions.
Classified as a micronutrient, Cl- is required by all plants in small quantities. Stomata regulate the release of moisture from plants so they can minimize water loss during stressful dry periods. Chloride is key in stomatal regulation. Chloride is involved in the chemical breakdown of water in the presence of sunlight and activates several enzyme systems. Chloride plays an important role in plants as they acclimate to changing water availability (or make osmotic adjustments). Chloride supports the transport of nutrients such as calcium, magnesium and potassium within a plant. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses. CHLORINE
Micronutrient
Stomatal Regulation
Chemical Breakdown of H₂0
Osmotic Adjustments
Transport of Nutrients
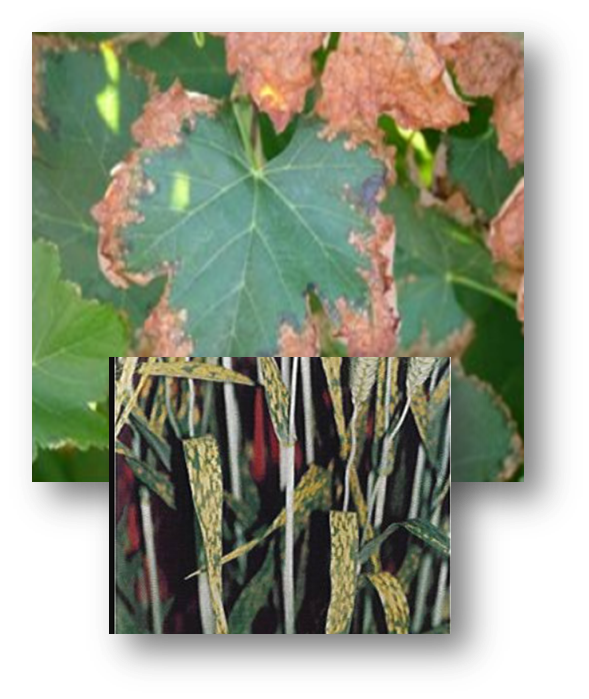
Chlorine deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.