KNOW MORE
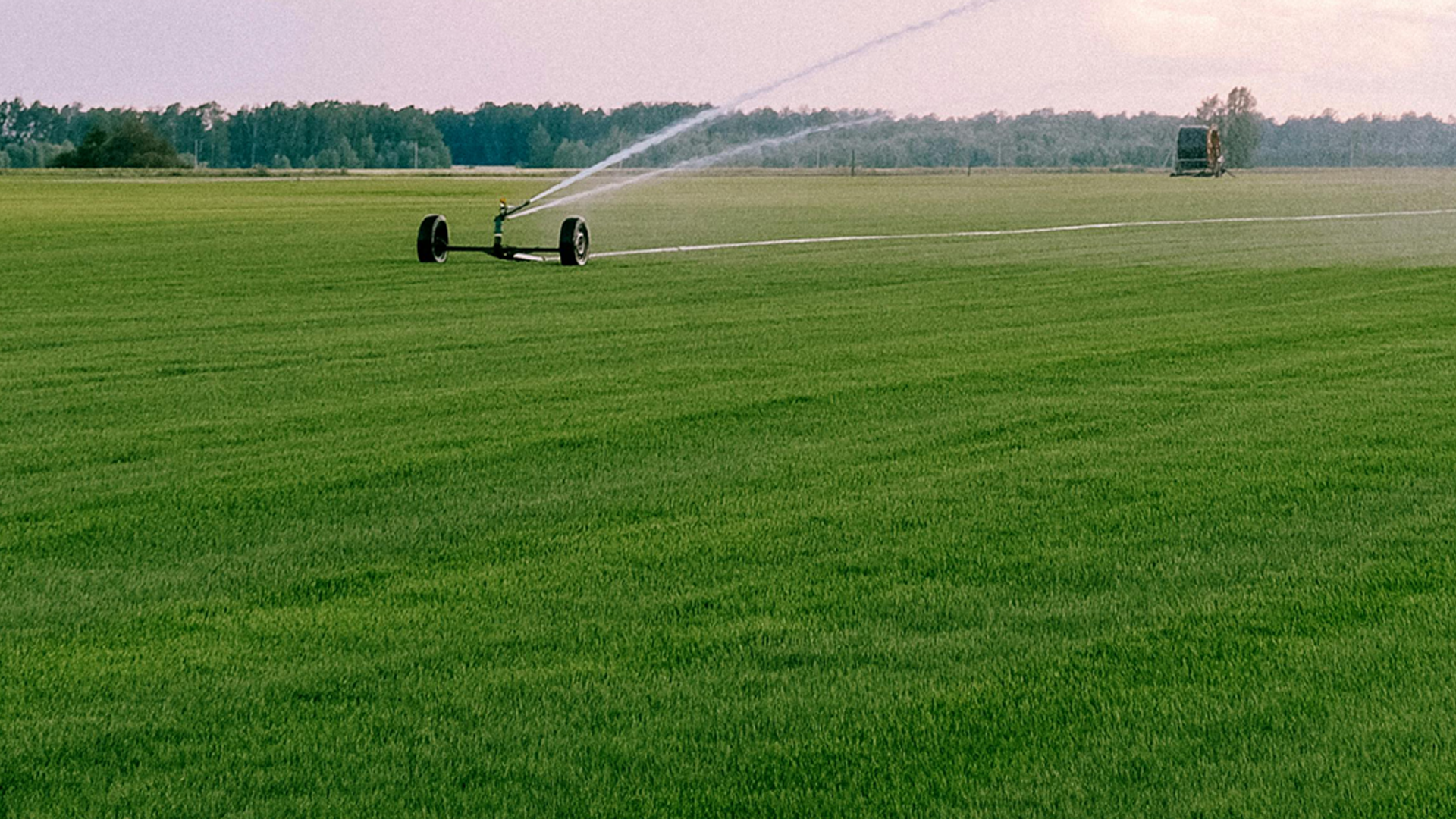
Exogenous application of soluble zinc sources, similar to fertilizer application, has been advocated to various crops. About 96 to 99% of the applied zinc is converted into different type of insoluble forms depending upon the soil types, physico-chemical reactions of the soil. The solubility of zinc is highly dependent on soil pH and moisture. Zinc occurs in soil as ores of augite, biotite, hornblende, olivine and sphalerite. However, availability of zinc from these sources is guided by many factors among which biochemical actions of rhizosphere microorganisms play an important role in converting such unavailable sources into available ones (Bhupinder et al., 2005). The zinc thus made unavailable can be reverted back to available form by application of bacterial strain capable of solubilizing it. Bacteria are known to immobilize zinc metal by precipitation and adsorption. The capability to dissolve immobilized zinc i.e. zinc carbonate, zinc oxide and zinc phosphate in appreciable quantity is not universal feature amongst the cultivable bacteria on soil surface. Few zinc solubilizing bacterial genera viz., Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans, Acinetobacter sp., Bacillus sp., Gluconacetobacter sp., Pseudomonas sp. and facultative thermophilic iron oxidizers were reported as zinc solubilizers. These bacteria improve the plant growth and development by colonizing the rhizosphere and by solubilizing complex zinc compounds into simpler ones, thus making zinc available to the plants. Zinc solubilizing microorganisms solubilize zinc through various mechanisms, one of which is acidification.Thiobacillus thioxidans
Bio-Zn
Zinc Solubilizing Bacteria
Zinc is an imperative micronutrient required for optimum plant growth. Zinc solubilizing bacteria are potential alternatives for zinc supplementation and convert applied inorganic zinc to available forms.Thiobacillus thiooxidans is a bacterium that can help make zinc available to plants by oxidizing zinc in soil and producing organic acids that mobilize zinc. This can be an alternative to zinc supplements and can be used on a variety of crops, including vegetables, cereals, and fruits. these bacteria ensure a daily supply of zinc to the plants.
Major Role
plant growth and development
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.