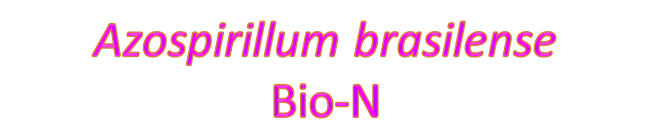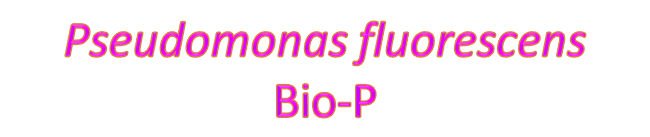KNOW MORE

Manganese (Mn) functions primarily as part of enzyme systems in plants. It activates several important metabolic reactions and plays a direct role in photosynthesis.
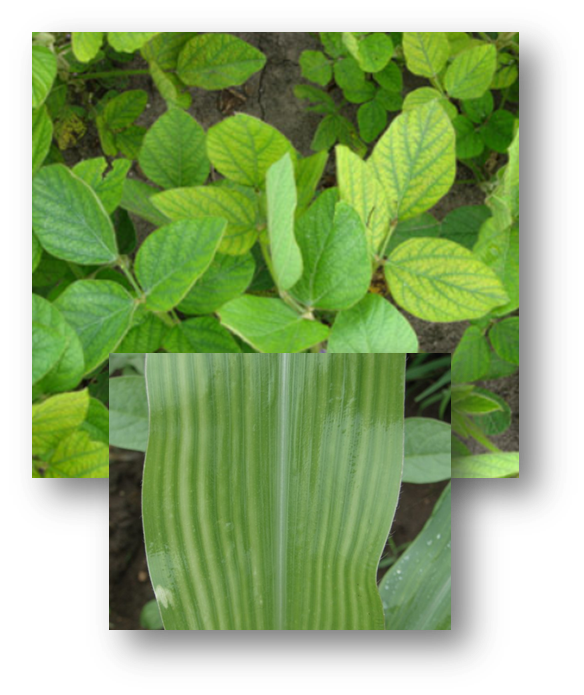
Manganese accelerates germination and maturity while increasing the availability of phosphorus (P) and calcium (Ca). Manganese plays a vital role in photosynthesis by aiding in chlorophyll synthesis. Soybeans and wheat in particular require more Mn than many crops. Manganese is very immobile in plants, so deficiency symptoms appear first on younger leaves, with yellowing between the veins. Sometimes a series of brownish-black specks appear. Although Mn deficiencies are often associated with high soil pH, they may result from an imbalance with other nutrients such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and Iron (Fe). Manganese deficiencies are most common in high organic matter soils and in those soils with naturally low Mn content and neutral to alkaline pH. Symptoms of deficiency can vary across crop species, but similarities exist for how nutrient insufficiency impacts plant tissue color and appearance. Nutrient deficiencies are commonly associated with the physical location on the plant (i.e., whether the symptoms are primarily observed on older versus newly formed plant tissue), but these symptoms can spread as the severity of the deficiency progresses. MANGANESE
Micronutrient With Giant Benefits
Photosynthesis
More Mn
Deficiency Symptoms
Imbalanced Nutrients
Soils with Mn Deficiencies
Manganese deficiency symptoms
PLANTAUX
MICRO-NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
MACRONUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
SECONDARY NUTRIENT

PLANTAUX
BIO-FERTILIZERS / BIO-CONTROL AGENTS
Always read and follow label directions. . Results may vary depending on soil, climate or other conditions.
© 2024.All rights reserved. PLANTAUX.